Contents
Do you remember that your mother cleaned the house thoroughly in the springtime? Spring cleaning is an annual cleaning of the house for many households. We thoroughly clean every part of the house and prepare it for the coming season.
Similarly, industrial systems also require a thorough cleaning which is never better than spring. General cleaning is important to save the compressed air system from damaging or poor performance, but don’t forget to do thorough maintenance of the system and prepare it for the rising temperatures.
What is a Screw Air Compressor?
What is a Screw Air Compressor?
Here is a checklist before you allow the compressed air system to run during the season. It’s a yearly maintenance plan that you must do in the spring.
Regulate the required voltage
Start with the voltage of the compressed air system. Check if it is getting the right voltage that is required by the system. Notice that the voltage must be optimal, neither higher nor lower than the required value.
If the voltage is higher than that required by the compressor, it will cause damage to the system and cost you more. On the other hand, if the voltage is too low than what is required for the machine to work properly, it will end up in an inefficient system that is not producing the desired results.
On average, an electric air compressor needs 110 to 120V, while a motor-run air compressor needs 220V. Regulate the voltage of your system according to its type and model.
Monitor temperature
Another important thing to check is the temperature of any electronic machine. The optimal temperature for a compressed air system should range between 50 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit.
Below this temperature, the system will lead to freezing, and above this temperature, it will end up overheating. In most cases, overheating is an issue. So check for overheating especially when preparing your machine for the summer season.
For this, you might inspect the cooling systems of the compressor. Two different types of compressed air systems use different cooling strategies; i.e., water cooling and air cooling. Moreover, heat exchangers in the system are an additional source to deal with this issue.
Check the reliability of these cooling systems and fix them so that your system does not overheat in summer. Also, check for any clogged pipes or vents which may be causing the temperature of the system to rise.
Navigate the compressor oil
After checking voltage and temperature, check if the oil of the compressed system is sufficient or not. Lubrication is an important part of machinery when it comes to its efficiency. Even when you have maintained each part of the air compressed system but ignored its lubrication, the system will be at risk of inefficiency.
It is important to assess that the oil needs to get replaced, otherwise it will cause the varnish to build up and overheat the system. When any part of the air-compressed system is poorly lubricated, it will struggle to perform effectively and end up overheating the system.
Varnish is the byproduct of oil degradation in the oil-based air compressed system. It usually happens when the oil is not changed for a long time and it starts degenerating.
Regardless of whichever high-quality lubricant you’re using, there are 99.9 chances of degradation. Poor lubrication, overheating, and varnish buildup is a vicious cycle that needs to be assessed timely to prevent more serious outcomes.
The oil change is a part of the yearly maintenance of the compressed system and there’s no time better than spring to nourish your system to work efficiently in summer. On average, you must do this after at least 1000 hours of usage.
Test the reliability of filters
Testing the filters is an important task in spring as the season comes and leaves with a lot of airborne particles that clog filters and cause problems in the flow of air. In this way, the working of the compressed air system compromises and ultimately increases costs.
Spring is the season that puts more stress on the filters to screen pollens and other tiny air particles. So changing the dirty and clogged filters in spring is a good idea to welcome the new season.
For changing the filters, unplug the machine and let it cool down. Then remove the top base and check the filter element thoroughly. Dust off the debris of the filter and make sure they are clean. If they are still not clean or you notice any clogged pores, replace the filters.
On average, filters should be changed after 2000 hours of usage. Don’t forget to check the oil filter as well if your compressor is oil-based.
Investigate if there are any leaks
Despite the fact that the compressor is the main part of an air compressed system, we can not overlook hose, pipes, and connectors. If the pipes are damaged or have holes in them, a rapid drop in pressure can occur without knowing the apparent cause of the misconduct.
A drop in PSI will increase the air demand and increase the overall cost. Not only this, but it will give a tough time to the compressor in producing efficient outcomes. Usually, air compressors come with a safety alarm if there is a severe drop in pressure. However, sometimes the leaks are too few to beep the safety alarm.
Still, you can not ignore these leaks as a small leak can cause drastic effects on your electricity bills. In such a case, you have to figure out the leakages yourself by following the look, listen and feel rule.
To detect the leaks, turn off the machine and stand closer to it. Carefully listen to any sound near the system and you’ll detect the leakage. Fix the leakage if any and tighten the connections to avoid energy wastage.
Drain the receiver tank
The receiver tank has served a lot the whole year. It would been full of water vapors until now. If you leave it as it is, the upcoming season loaded with humidity will be quite difficult for the compressor tank.
Clean the tank and drain out those vapors causing inefficiencies in the system. Open the drain valve by rotating the drain ring in a clockwise direction. Then clear out all the content present in the drain and let it air dry. After it is completely dry, seal the valve with the ring again.
Check if the safest option is working
The last thing you must check to quote the air-compressed system ‘ready for summer’ is checking its safety. Test if the auto-shutdown option is working. Also, make sure the performance of safety alarms.
Recommend Products
2~40bar Oil free Screw air compressor
8~12bar Oil-free Scroll air compressor
2~16bar oil lubricated screw air compressor
Choosing the Right Air Compressor For Your Home
You will find that air compressors are indispensable tools for a variety of situations, including garages, home workshops, and basements. These tools can power a variety of tools, and each model is sized to suit the job at hand. Because air compressors have only one motor, they are lightweight, compact, and easy to handle. Using one air compressor to power several tools will also reduce the wear and tear on individual components. This article will introduce some important characteristics to look for when choosing the right air compressor for your home.
Positive displacement
A positive displacement compressor applies pressure to a fluid, whereas a centrifugal one does the opposite. A positive displacement compressor creates the desired pressure by trapping air and increasing its volume. Its discharge valve releases the high-pressure gas. These compressors are used in industrial applications and nuclear power plants. The difference between a positive and negative displacement compressor is that a positive displacement compressor can compress and release air at a consistent rate.
A positive displacement air compressor uses a reciprocating piston to compress air. This reduces the volume of the air in the compression chamber, and a discharge valve opens when the pressure reaches the desired level. These compressors are used in bicycle pumps and other pneumatic tools. Positive displacement air compressors have multiple inlet ports and have several configurations. Positive displacement air compressors have a single-acting and double-acting piston, and can be oil-lubricated or oil-free.
A positive displacement air compressor is different from a dynamic compressor. It draws air into the compression chambers and then releases the pressure when the valve is opened. Positive displacement compressors are common in industrial applications and are available in single-acting, double-acting, and oil-lubricated models. Large piston compressors have ventilated intermediate pieces and crossheads on gudgeon pins. Smaller models have permanently sealed crankcases with bearings.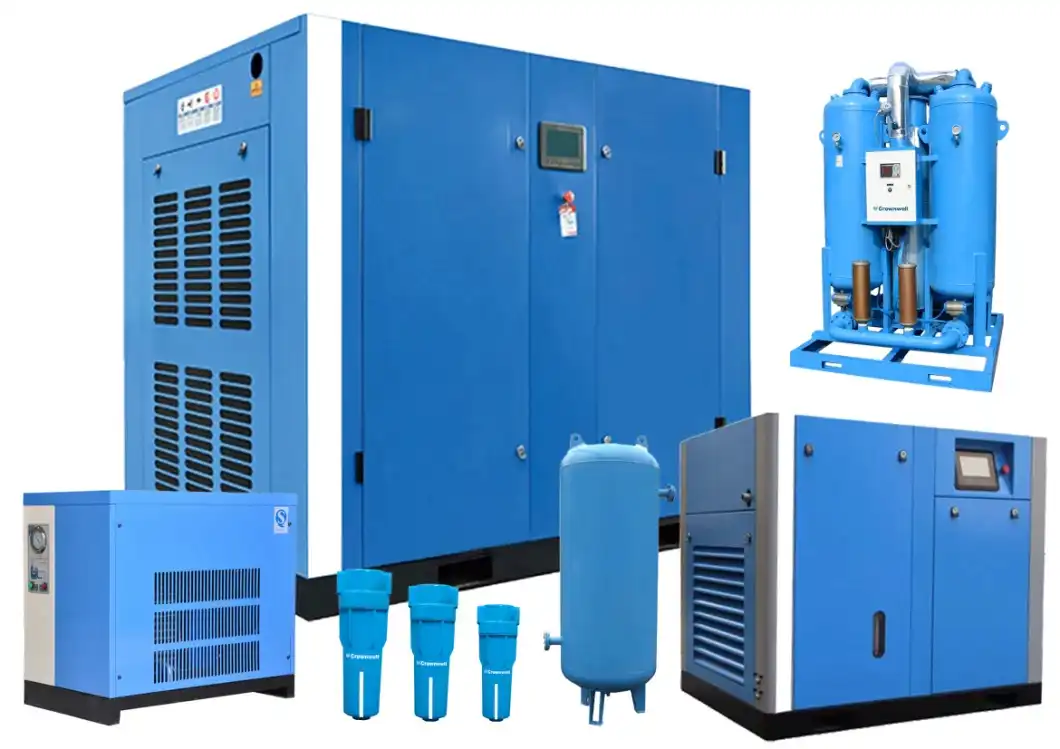
Oil-free
Oil-free air compressors have some advantages over their oil-lubricated counterparts. They do not require lubrication oil because they are coated with Teflon. The material has one of the lowest coefficients of friction and is layered, so it slides past other layers with little effort. Because of this, oil-free compressors tend to be cheaper and still deliver comparable performance. Oil-free compressors are a good choice for industrial applications.
The life of an oil-free air compressor is significantly longer than an oil-lubricated counterpart. These models can operate up to 2,000 hours, four times longer than the average oil-lubed compressor. Oil-free compressors also have a significantly lower operating noise than their oil-lubricated counterparts. And because they don’t need oil changes, they are quieter. Some even last up to 2,000 hours.
An oil-free air compressor is a good choice if your application requires high levels of purity. Several applications require ultra-pure air, and even a drop of oil can cause product spoilage or damage to production equipment. In addition to the health risks, an oil-free air compressor reduces the costs associated with oil contamination and minimizes leaks. It also eliminates the need for oil collection, disposal, and treatment.
A typical oil-free air compressor is very efficient, requiring only about 18% of the full load horsepower. However, oil-free compressors have a higher risk of premature failure and are not recommended for large-scale industrial applications. They may also use up to 18% of the compressor’s full capacity. They may sound appealing, but you must make sure you understand the benefits of an oil-free air compressor before choosing one for your industrial applications.
Single-stage
A single-stage air compressor is designed to provide the power for a single pneumatic tool or device. These machines are generally smaller than two-stage compressors and produce less heat and energy. These machines aren’t designed for heavy-duty industries, but they are still highly effective for a variety of applications, including auto shops, gas stations, and various manufacturing plants. They can also be used in borewells, as they are suitable for small spaces with low air flow requirements.
A single-stage air compressor has one cylinder and two valves – the inlet and the delivery valves. Both of these valves function mechanically, with the inlet valve controlling torque and the delivery one controlling air pressure. Generally, single-stage compressors are powered by a gas engine, but there are also electric models available. The single-stage air compressor is the most common type of air compressor. It has a single cylinder, one piston, and one air cylinder.
The single-stage air compressors are used for small projects or personal use. A two-stage air compressor is more effective for industrial projects. Its longer air end life makes it more efficient. It is also more efficient for use in the automotive industry, where the engine has many cylinders. In general, single-stage compressors require a higher power level. The single-stage model is ideal for small projects, while a two-stage one is suitable for larger-scale arsenals.
CFM
The cubic foot-per-minute (CFM) of an air compressor is the output of the machine. In order to calculate the CFM level, start by looking at the compressor’s specifications. You should know how many cubic feet the unit can hold and how many pounds per square inch it can compress. Once you have these information, you can calculate the CFM. Now you can use these numbers to select an appropriate air compressor for your needs.
The most common way to increase the CFM of an air compressor is to turn the regulator down. By turning the dial down, the air compressor will produce more than 10 CFM. You can also try connecting two output valves. Make sure that the settings are adjusted properly before you begin. This will ensure that your air compressor is functioning at its maximum efficiency and lifespan. To increase the CFM of your air compressor, first check that your regulator is calibrated for the desired pressure level.
To calculate the CFM of an air compressor, first determine the tank volume of the machine. Then, multiply this volume by the time it takes to fill the tank. Then, divide the result by 60 seconds to calculate the CFM. Once you know how much air your machine can hold, you can choose a suitable air compressor. If you’re working in a confined area, you should buy a tool with a large tank.
PSI
The PSI of an air compressor is the pressure that it can output. A typical air compressor has a gauge connected to the airline at the bottom, next to it, or between the two. The gauge tells the actual pressure of the air compressor, while the cut-out pressure is determined by the manufacturer. The manufacturer recommends that you set the cut-out pressure twenty to forty PSI higher than the factory recommended pressure. If you want to set the pressure for your nail gun, you can use the cut-in and cut-out pressures on your compressor, and the tank won’t exceed this range.
The PSI of an air compressor measures the force that it can deliver, which is often in pounds per square inch. For most air tools, you need at least forty to 90 psi. In general, reciprocating air compressors work on an on/off basis. This relationship is known as the duty cycle. All air compressors are rated for a particular duty cycle, such as fifty percent on and twenty-five percent off.
The Psig of an air compressor is not free, as many people believe. The PSI of an air compressor is not free, but it is essential to maintain it for safe operations. If you’re having trouble maintaining a consistent pressure, consider turning down the PSI of your compressor by 2 psig. This will determine the critical pressure for the machine. You’ll also increase the amount of energy in the system by one percent.
Power source
The power source for an air compressor is crucial in its operation. Without the correct voltage and amperage, air compressors will not function properly. The power source must be close to the compressor so that it can plug into an electrical outlet. If it is too far from the outlet, the compressor may not be able to build enough pressure. When this happens, the fuse inside the air compressor will turn off to protect the user. The power source should be a safe distance from the compressor.
Most manufacturers do not specify the power source for an air compressor. Depending on the horsepower, the compressor will require approximately four amps of power. A one-horsepower compressor would draw about twelve amps. If it were powered by a typical 120-volt household supply, its motor would exceed the 15-amp breaker capacity. A larger air compressor, however, will require a separate 15-amp power source, making it impossible to use it with this type of power source.
The power source for an air compressor is typically electrical alternating current (AC) that is equivalent to the voltage on a standard wall outlet. A three-phase air compressor, on the other hand, requires a special AC supply with three electrical offset pulses. Regardless of the type of air compressor, the power source must be compatible with the incoming power service. One of the most common problems when attempting to connect an air compressor to an AC power source is undersized wire. This results in low voltage and high amperes, tripping of over-load relays and blown fuses.



